react-router-dom
作者:高天阳
邮箱:[email protected]
更改历史
* 2019-09-02 高天阳 初始化文档
1. 背景
react-router-v4,我称之为“第四代react-router”,react-router和react-router-dom的区别是什么呢?
为什么有时候我们看到如下的写法:
写法1:
import {Swtich, Route, Router, HashHistory, Link} from 'react-router-dom';
写法2:
import {Switch, Route, Router} from 'react-router';
import {HashHistory, Link} from 'react-router-dom';
先简单说下各自的功能:
react-router: 实现了路由的核心功能
react-router-dom: 基于react-router,加入了在浏览器运行环境下的一些功能,
例如:Link组件,会渲染一个a标签,
Link组件源码a标签行;
BrowserRouter和HashRouter组件,前者使用pushState和popState事件构建路由,
后者使用window.location.hash和hashchange事件构建路由。
react-router-native: 基于react-router,类似react-router-dom,加入了react-native运行环境下的一些功能。
从源码层面来说明:
首先看react-router-dom中的Switch组件的源码
// Written in this round about way for babel-transform-imports
import { Switch } from 'react-router'
export default Switch
只是从react-router中导入Switch组件,然后重新导出而已。
通过查看其他模块的源码,Route组件的源码、Router组件的源码发现,和Swtich一样,都是从react-router中导入了相应的组件,
重新导出而已,并没有对实现做什么特殊处理。
结论:
react-router-dom依赖react-router,所以我们使用npm安装依赖的时候,只需要安装相应环境下的库即可,不用再显式安装react-router。
基于浏览器环境的开发,只需要安装react-router-dom;基于react-native环境的开发,只需要安装react-router-native。
npm会自动解析react-router-dom包中package.json的依赖并安装。
react-router-dom中package.json依赖:
"dependencies": {
"history": "^4.7.2",
"invariant": "^2.2.2",
"loose-envify": "^1.3.1",
"prop-types": "^15.5.4",
"react-router": "^4.2.0",
"warning": "^3.0.0"
}
安装了react-router-dom,npm会解析并安装上述依赖包。可以看到,其中包括react-router。
所以,回到最开始的写法。基于浏览器环境的开发,写法1就可以了。
2. 如何选用
react-router-dom 比前者多出了 <Link>、<BrowserRouter> 这样的 DOM 类组件。
因此我们只需引用 react-router-dom 这个包就行了。当然,如果搭配 redux ,你还需要使用 react-router-redux。
3. 核心
3.1. HashRouter和BrowserRouter
HashRouter 和 BrowserRouter 像是一个 box 所有的 route 都需要放在里面。
3.2. HashRouter
HashRouter 是通过 hash 值来对路由进行控制。使用 HashRouter,路由会默认有个#。
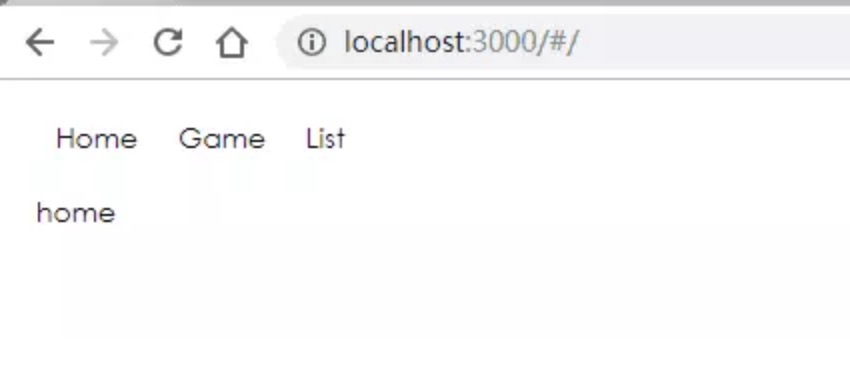
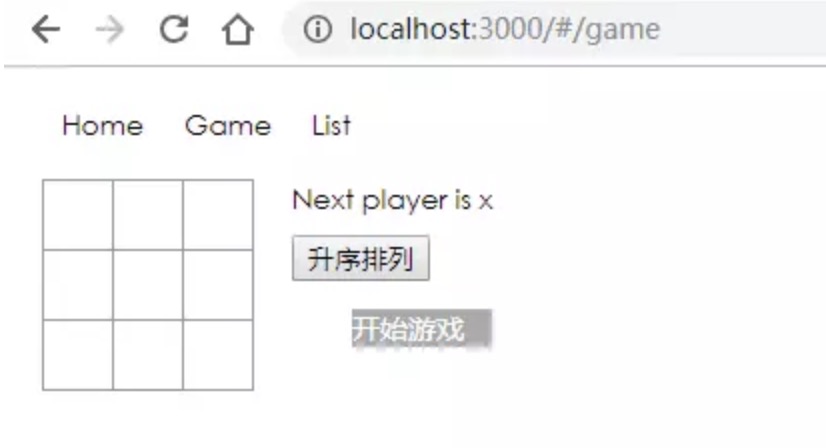
ReactDOM.render(
<HashRouter>
<div>
<Nav />
<Route exact path='/' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/game' component={Game}></Route>
</div>
</HashRouter>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
小游戏详见: react 三子棋小游戏
3.3. BrowserRouter
BrowserRouter 使用了 HTML5 history API,保证 UI 界面和 URL 保持同步。使用 BrowserRouter ,路由不会有个#。
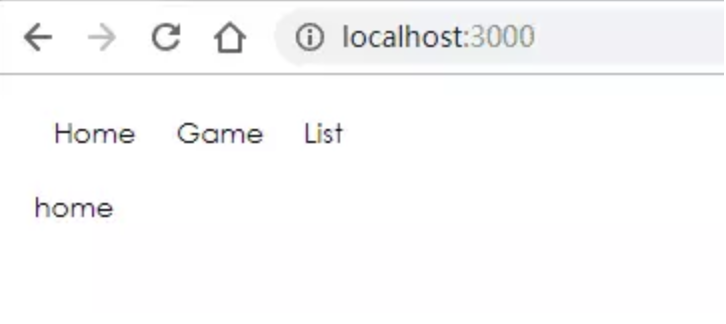
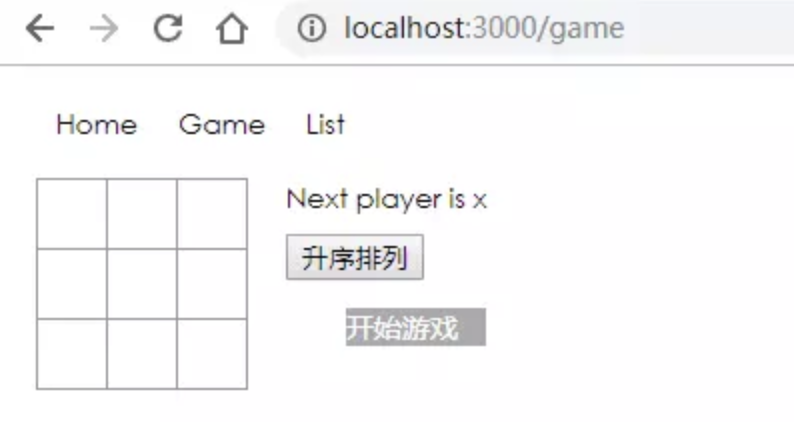
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<div>
<Nav />
<Route exact path='/' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/game' component={Game}></Route>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
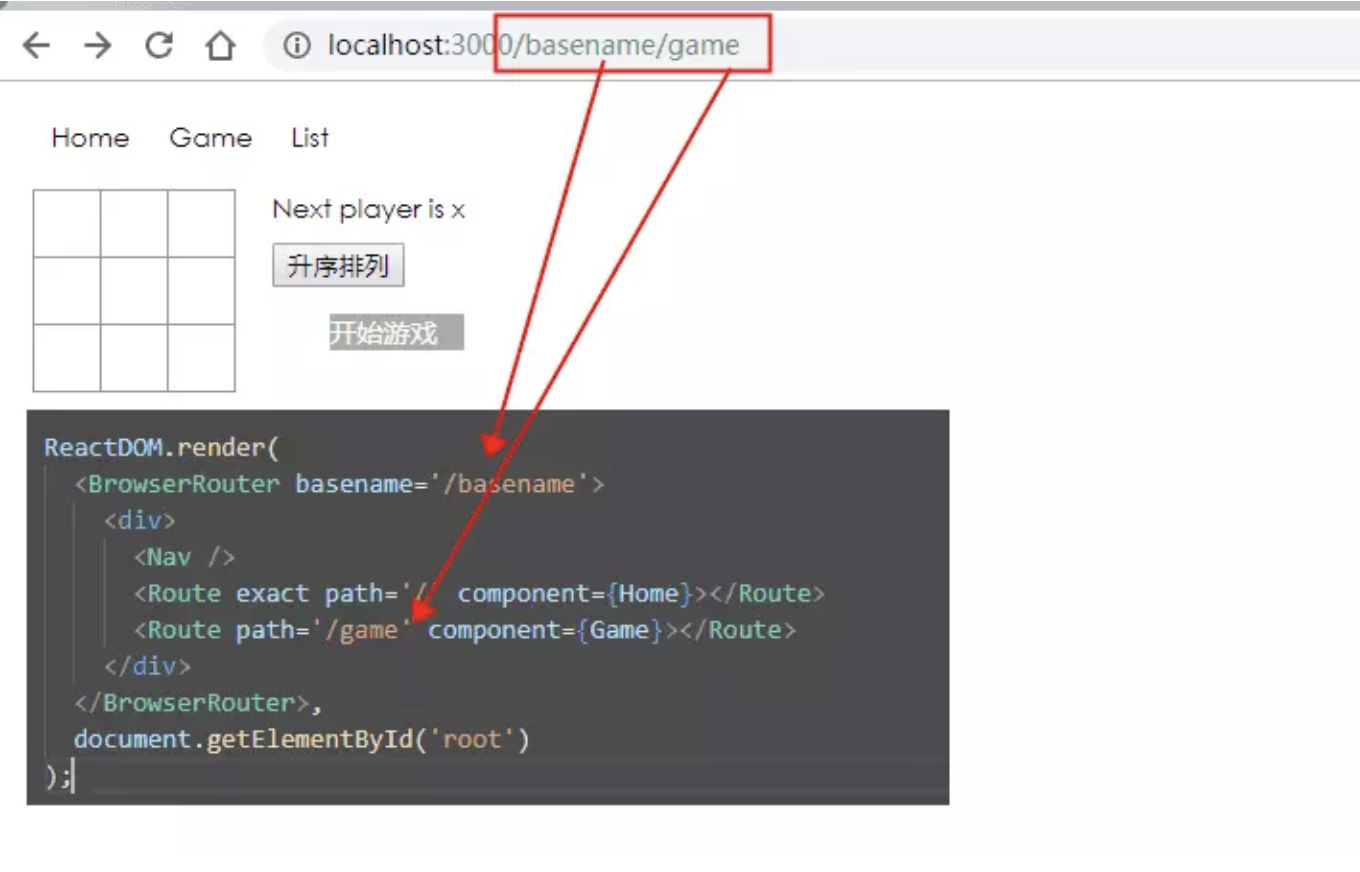
basename: string
为所有位置添加一个基准URL,当需要把页面部署到服务器的二级目录时,可以使用 basename 设置到此目录。
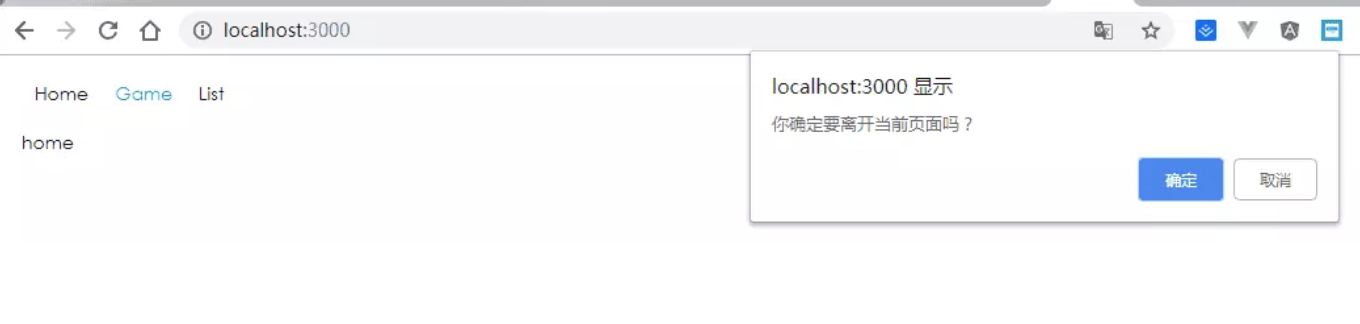
getUserConfirmation: func
导航到此页面前执行的函数,默认使用 window.confirm (需同 Prompt 配合使用)
此为默认行为
const getConfirmation = (message, callback) => {
const allowTransition = window.confirm(message);
callback(allowTransition);
}
// ========================================
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter getUserConfirmation={getConfirmation}>
<div>
<Prompt message="你确定要离开当前页面吗?" />
<Nav />
<Route exact path='/' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/game' component={Game}></Route>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
传送门:react-history
forceRefresh: bool
若为 true,导航过程中会刷新整个页面。多在不支持 HTML5 history API 的浏览器中使用此功能。
keyLength: number
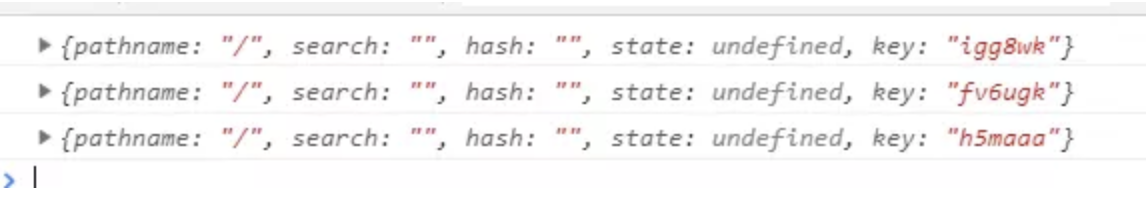
设置它里面路由的 location.key 的长度。默认是6。(key:点击同一个链接时, location.key 都会改变。)
this.props.location
children: node
渲染唯一子元素,React组件自带 children 属性。
传送门:react.children属性
3.4. Route
控制路径对应显示的组件
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<div>
<Nav />
<Route exact path='/' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/game' component={Game}></Route>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
3.5. Route render methods
- <Route component>
- <Route render>
- <Route children>
同一个 <Route> 应该只使用一种渲染方法 ,大部分情况下使用 component 。
component
只有访问地址和路由匹配时,才会渲染 React 组件。Router 将根据指定的组件,
使用 React.createElement 创建一个新的 React 元素。(如果你向 component 提供一个内联函数,
那么每次渲染都会创建一个新组件,这将产生不必要的重复装载)
render
可以方便地进行内联渲染和包装,而无需进行不必要的组件重装。传入一个函数,在位置匹配时调用,
而不是使用 component 创建一个新的 React 元素。
警告:<Route component> 优先于 <Route render>,因此不要在同一个 <Route> 中同时使用两者。
children
无论 path 是否匹配都可以渲染,除此之外,它的工作原理与 render 完全一样。
路由与 URL 不匹配时 match 为 null。因此,可以根据路由是否匹配,动态地调整用户界面。
const ListItemLink = ({ to, ...rest }) => (
<Route path={to} children={({ match }) => (
<li className={match ? 'active' : ''}>
<Link to={to} {...rest} />
</li>
)} />
)
<ul>
<ListItemLink to="/somewhere" />
<ListItemLink to="/somewhere-else" />
</ul>
警告:<Route component> 和 <Route render> 优先于 <Route children>,因此不要在同一个 <Route> 中同时使用多个。
3.6. Route render methods
三种渲染方式都将提供相同的三个路由属性
matchlocationhistory
match
match 是在使用 router 之后被放入 props 中的一个属性,
在 class 创建的组件中我们需要通过 this.props.match 来获取 match 之中的信息。

<BrowserRouter>
<div>
<Nav />
<Route exact path='/' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/game/:id' component={Game}></Route>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
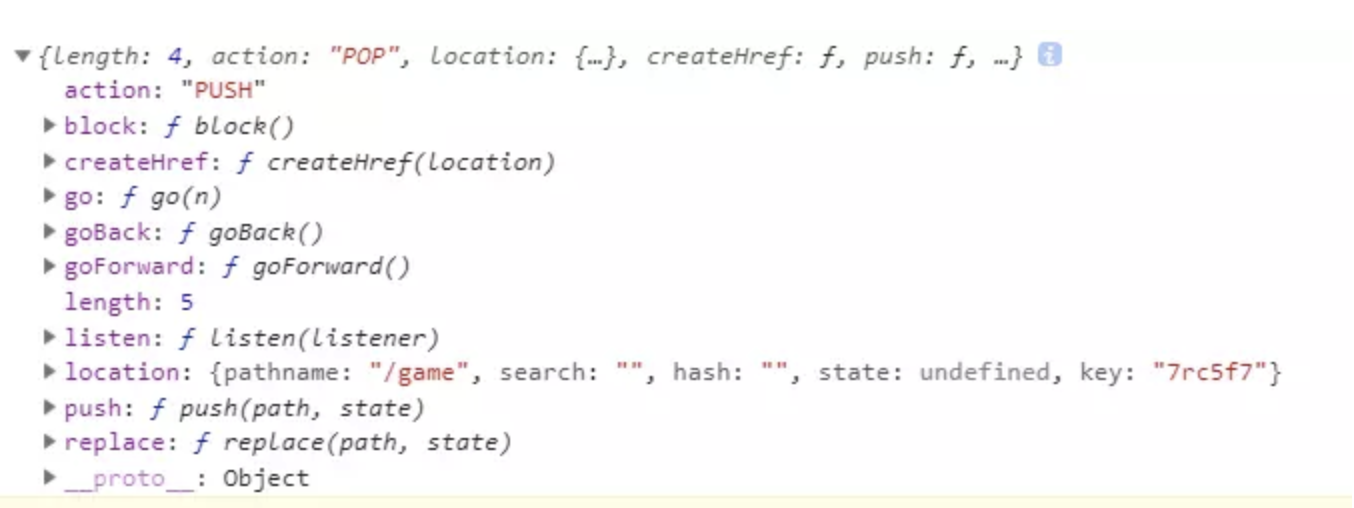
history
它提供了很多有用的方法可以在路由系统中使用。
location
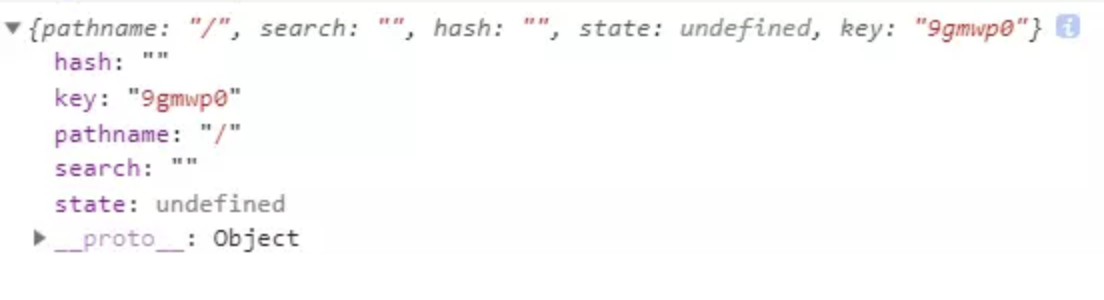
它可以认为是 URL 的对象形式表示。
path: string
可以是 path-to-regexp 能够理解的任何有效的 URL 路径。
没有定义 path 的 <Route> 总是会被匹配。
exact: bool
如果为 true,则只有在 path 完全匹配 location.pathname 时才匹配。
| exact | path | location.pathname | matches? |
|---|---|---|---|
| true | /home | /home/list | no |
| false | /home | /home/list | yes |
strict: bool
如果为 true,则具有尾部斜杠的 path 仅与具有尾部斜杠的 location.pathname 匹配。
| path | location.pathname | matches? |
|---|---|---|
| /home/ | /home | no |
| /home/ | /home/ | yes |
| /home/ | /home/list | yes |
sensitive: bool
如果为 true,进行匹配时将区分大小写。
| sensitive | path | location.pathname | matches? |
|---|---|---|---|
| true | /home/ | /home | yes |
| true | /Home/ | /home | no |
| false | /Home | /home | yes |
4. Link VS NavLink
两者都是可以控制路由跳转的,而 NavLink 的 api 更多
4.1. Link
提供声明式的、可访问的导航链接。
to: string
一个字符串形式的链接地址
<Link to='/courses?sort=name' />
to: object
一个对象形式的链接地址,可以具有以下任何属性:
pathname- 要链接到的路径search- 查询参数hash- URL 中的 hashstate- 存储到 location 中的额外状态数据
<Link to={{
pathname: '/courses',
search: '?sort=name',
hash: '#the-hash',
state: {
fromDashboard: true
}
}} />
replace: bool
当设置为 true 时,点击链接后将替换历史堆栈中的当前条目,而不是添加新条目。默认为 false。
(当点击返回时将找不到设置为 true 的页面)
<Link to='/'>Home</Link>
<Link to='/game' replace>Game</Link>
<Link to='/list'>List</Link>
一次跳转 / => /game => /list => /
点击返回 / => /list => /
innerRef: func
允许访问组件的底层引用。
4.2. NavLink
一个特殊版的 Link,它会在与当前 URL 匹配时为其呈现元素添加样式属性。 (其实就是像为页面导航准备的。因为导航需要有 “activated state”。)
activeClassName: string
当元素处于 activated state 时应用的类,默认为 active。与 className 属性一起使用。
activeStyle: object
当元素处于 activated state 时应用的样式。
exact: bool
如果为 true,则只有在位置完全匹配时才应用 activated 类/样式。
strict: bool
如果为 true,则在确定位置是否与当前 URL 匹配时,路径名后面的斜杠。
isActive: func
添加额外逻辑以确定链接是否处于激活状态的函数。
const oddEvent = (match, location) => {
if (!match) {
return false;
}
const eventID = parseInt(match.params.eventID);
return !isNaN(eventID) && eventID % 2 === 1;
}
<NavLink to="/events/123" isActive={oddEvent}>Event 123</NavLink>
location: object
isActive 默认比较当前历史位置(通常是当前的浏览器 URL)。
你也可以传递一个不同的 location 进行比较。
4.3. Prompt
跳转之前的一些确认信息。
message: string
当用户试图离开某个位置时弹出的提示信息。
message: func
将在用户试图导航到下一个位置时调用。需要返回一个字符串以向用户显示提示,或者返回 true 允许直接跳转。
when: bool
在应用程序中,你可以始终渲染 <Prompt> 组件,
并通过设置 when={true} 或 when={false} 以阻止或允许相应的提示,
而不是根据某些条件来决定是否渲染 <Prompt> 组件。
当它的值为
true时,会弹出提示信息。如果为false则不会弹出。
4.4. Redirect
<Redirect> 渲染时将导航到一个新地址, 这个新地址覆盖在访问历史信息里面的本该访问的那个地址(类似服务器端重定向)。
import { Route, Redirect } from 'react-router-dom';
<Route exact path="/" render={() => (
loggedIn ? (
<Redirect to="/dashboard" />
) : (
<PublicHomePage />
)
)} />
to: string
要重定向到的 URL 字符串,可以是 path-to-regexp 能够理解的任何有效的 URL 路径。
要使用的 URL 参数必须由 from 提供。
to: object
要重定向到的位置,其中 pathname 可以是 path-to-regexp 能够理解的任何有效的 URL 路径。
<Redirect to={{
pathname: '/login',
search: '?utm=your+face',
state: {
referrer: currentLocation
}
}} />
push: bool
如果为 true,重定向会将新的位置推入历史记录,而不是替换当前条目。
from: string
将要被重定向路径。所有匹配的 URL 参数都会提供给 to,必须包含在 to 中用到的所有参数,
未使用参数将被忽略。只能在 <Switch> 组件内使用 <Redirect from>
<Switch>
<Redirect from='/old-path' to='/new-path' />
<Route path='/new-path' component={Place} />
</Switch>
exact: bool
相当于 Route.exact。
strict: bool
相当于 Route.strict。
4.5. Switch
常常会用来包裹Route,它里面不能放其他元素, 用于渲染与路径匹配的第一个子 <Route> 或 <Redirect>。
这与仅仅使用列表形式的 <Route> 有何不同?
<Switch> 只会渲染一个路由。而单纯的 <Route> 列表, 每一个与路径匹配的 <Route> 都将包含在渲染范围内。
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/:user" component={User} />
<Route component={NoMatch} />
如果 URL 是 /about,那么 <About>、<User> 和 <NoMatch> 将全部渲染,
因为它们都与路径匹配。这将允许我们以很多方式将 <Route> 组合成我们的应用程序,
如侧边栏和面包屑、引导标签等。
但如果我们只想选择一个 ·<Route>· 来呈现。比如我们在 URL 为 ·/about· 时不想匹配 /:user, 就是可以通过 <Switch> 实现
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/:user" component={User} />
<Route component={NoMatch} />
</Switch>
location: object
用于匹配子元素而不是当前历史位置(通常是当前的浏览器 URL)的 location 对象。
children: node
所有 <Switch> 的子元素都应该是 <Route> 或 <Redirect>。 只有第一个匹配当前路径的子元素将被呈现。
<Route> 组件使用 path 属性进行匹配,而 <Redirect> 组件使用它们的 from 属性进行匹配。
(没有 path 属性的 <Route> 或者没有 from 属性的 <Redirect> 将始终与当前路径匹配。)
如果给 <Switch> 提供一个 location 属性,它将覆盖匹配的子元素上的 location 属性。
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/users" component={Users} />
<Redirect from="/accounts" to="/users" />
<Route component={NoMatch} />
</Switch>